Year 12 (AS level)
You start this year by studying the PH1 module with WJEC. This includes the following topics:
Basic Physics (units; scalars and vectors; forces; free body diagrams; moments; centre of gravity and equilibrium) (JG)
Kinematics (rectilinear motion - distance and displacement; speed; velocity; displacement/time graphs; velocity/time graphs; suvat; terminal velocity; centripetal acceleration) (JG)
Conduction of Electricity – Electric charge; Electric current; Nature of charge carriers in conductors. (RC)
Resistance – Relationship between current and potential difference; Resistance; Resistivity; Variation of resistance with temperature for metals; Superconductivity; Heating effect of an electric current. (RC)
D.C. Circuits – Series and parallel circuits; Combination of resistors; Internal resistance of sources; The potential divider.(RC)
Energy Concepts – Work; Energy and Power. (RC)
The initials after each topic tell you which teacher will be teaching the topic.
Year 12 (AS level)
PH2 consists of the following:
Waves – Progressive waves; Transverse and longitudinal waves; Polarisation; Frequency, wavelength and velocity of waves; Diffraction; Interference; Two-source interference patterns; Stationary waves. (RC)
Refraction of Light – Refraction; Wave Model of Refraction; Optical Fibre Communications. (JG)
Photons – The photoelectric effect; Photons; The electromagnetic Spectrum; Line emission and line absorption spectra; X-rays; Spontaneous and stimulated emission; Lasers – energy levels and structure; The semiconductor lasers and its uses. (RC)
Matter, Forces and the Universe – The nuclear atom; Leptons and quarks; Particle interactions; Conservation laws. (JG)
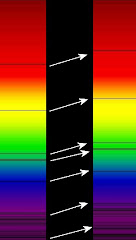
Using Radiation to Investigate Stars – Black-body radiation; Wien’s displacement law – stellar temperatures; Stefan’s law and stellar luminosity; Intensity and the inverse square law; Fraunhofer lines and stellar composition. (JG)
PH3 is the practical module and you will be doing this at the same time as you study PH2.
Year 13 (A2 level)
You will return in September to study PH4, which consists of the following:
Vibrations (circular motion; physical and mathematical treatment of undamped simple harmonic motion; energy interchanges during simple harmonic motion; damping of oscillations and free oscillations, forced oscillations and resonance) (RC).
Energy concepts (work, energy and power; internal energy; first law of thermodynamics and energy transfer) (JG)
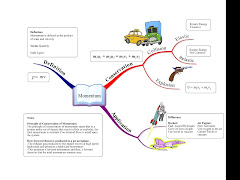
Momentum concepts (Linear momentum; Newton’s laws of motion and conservation of linear momentum and particle collision) (JG)
Molecular Kinetic Theory (Ideal gas laws and the equation of state; kinetic theory of gases; the kinetic theory of pressure of a perfect gas and the kinetic theory of a molecule) (JG)
Magnetic and Gravitational fields: Uniform and radial fields of force - the content of which is: electrostatic and gravitational fields; field strength (intensity); electrical and gravitational inverse square laws; potential in force fields; relation between intensity and potential gradient; vector addition of electrical fields; potential of a system of charges. (RC)
Alternating Currents (peak and r.m.s. values of sinusoidal quantities; vector treatment of alternating voltages and currents; effect of resistance, inductance and capacitance in a series circuit; phase lag and lead; resonance and use of the cathode ray oscilloscope) (RC)
The initials after each topic tell you which teacher will be teaching the topic.
You may find some of the links on this blog useful.
Year 13 (A2 level)
After your exams in January you will study PH5 - Fields, Forces and Nuclei.
Radioactivity and Radioiotopes with Mrs Goodwin - Studying Radioactive decay and the Decay Constant; Exponential decay and half lives; Nuclear equations and the uses of radioactivity - medical uses and generation of electricity, including hazards and safety precautions. (JG)
We will go on to study possibly the most famous equation in Physics - E = mc2; Binding energies; Fission and Fusion and Nuclear reactors. (JG)
Finally in this section we will examine Particle Physics. Including coherent scattering of em waves by charged particles; X-ray diffraction leading to molecular structure; Matter waves-electron and neutron diffraction; Production of high energy particles; Elastic scattering of alpha particles of heavy nuclei; Inelastic scattering of photons and particles by atoms, nuclei and nuclear constituents leading to atomic and nuclear structure. (JG)
Magnetic and Gravitational Fields. Uniform and Radial Fields of Force - the content of which is: Electrostatic and gravitational fields; Field strength (intensity); Electrical and gravitational inverse square laws; Potential in force fields; Relation between intensity and potential gradient; Vector addition of electrial fields; Potential energy of a system of charges. (RC)
Magnetic Fields (B-fields) including: Concept of magnetic fields; Force on a current-carrying conductor; Force on a moving charge; Magnetic fields due to currents; Effect of a ferrous core - relative permeability; Force between current-carrying conductors; Definintion of the ampere; Measurement of magnetic field strength (B); Deflection of beams of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields. (RC)
Electromagnetic Induction including: Magnetic flux; Laws of electromagnetic induction; Calculation of induced emf; Self induction. (RC)
Hi everyone, this blog is designed to help you to revise before your exams. Please remember that we are always available in school for you up to your exam and afterwards. If you need to ask a question at any other time you can ask it here and we'll get back to you.
Good luck with your revision!












5 comments:
Hi there Mrs G
Just happly revising Force and rotation in the revision sheets and came across this equation:
P1V1 = P2V2
I seem to remember something like it came up in the mock but I can't remember how to use it
Other than that everything else is going fine ;)
Thanks again Mrs G and see you soon
Mike
Hi Mike,
P is pressure and V is volume so this equation refers to Boyles law, one of the gas laws.
P1V1 is the pressure times the volume for the first situation, this is equal to the pressure times the volume for the second situation.
For example, in an airtight room, if we look at all the air in a room as situation 1 and then we squash the walls of the room in so that the room gets smaller, the pressure on the air molecules in the room increases just because the volume of the room gets smaller.
As pressure and volume are inversely proportional to each other the 2 sides of the equation are the same.
Using made up numbers:
P1V1 = P2V2
10x10 = 20x5
100 = 100
In the second case (situation 2) the pressure has increased because the volume has decreased but the overall value is still equal to situation 1's value.
Hope this makes sense. If you are still struggling come and see me after your next exam and I'll give you some more notes.
Talk to you soon,
best wishes
Mrs G.
Hey Mrs G
I feel I need a bit of help on half life equations. Could you reply or would it be better to speak to you first thing tomorrow.
I'm not sure what time my bus but it can range from 8.30 - 8.45 so I can't give a specific time
Many Thanks again
Mike
Hi Mike,
I'll be in my lab from 8.15 in the morning so come straight down and we'll go through your questions - no problem.
See you then,
Mrs G
Post a Comment